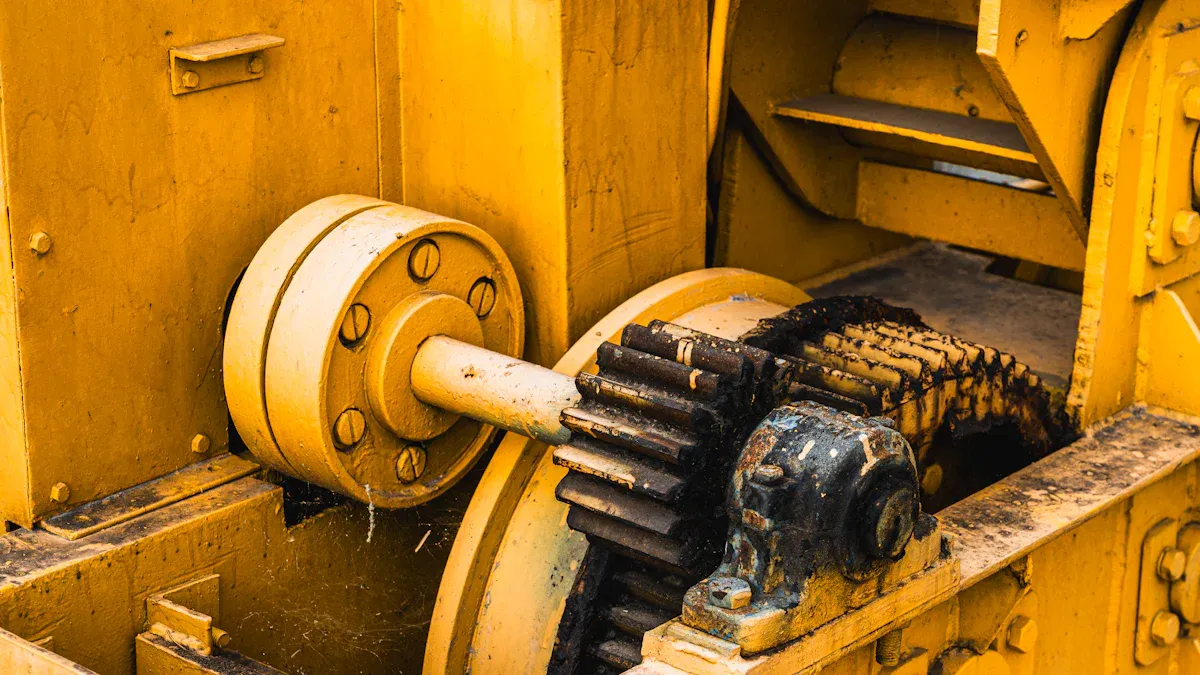
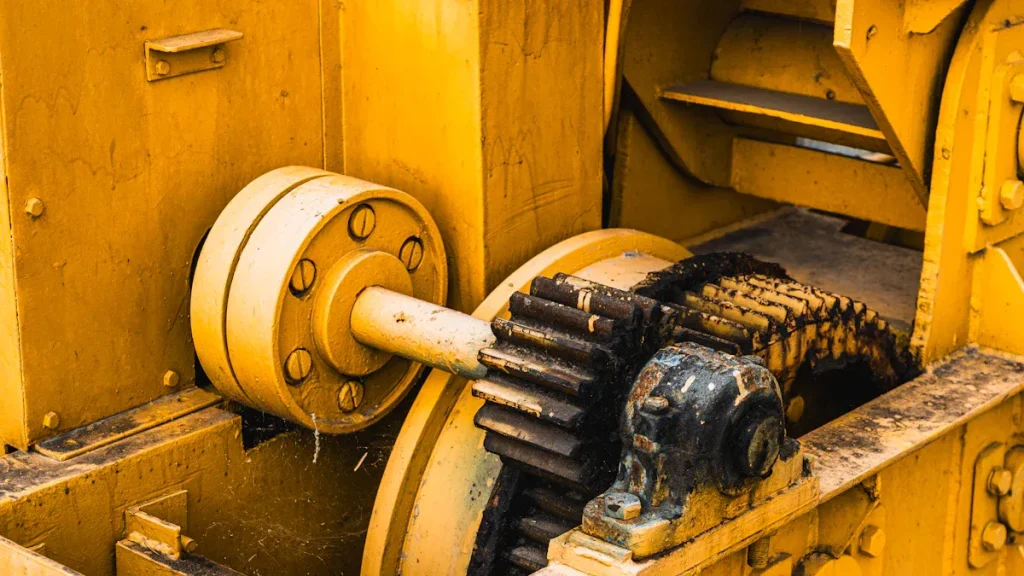
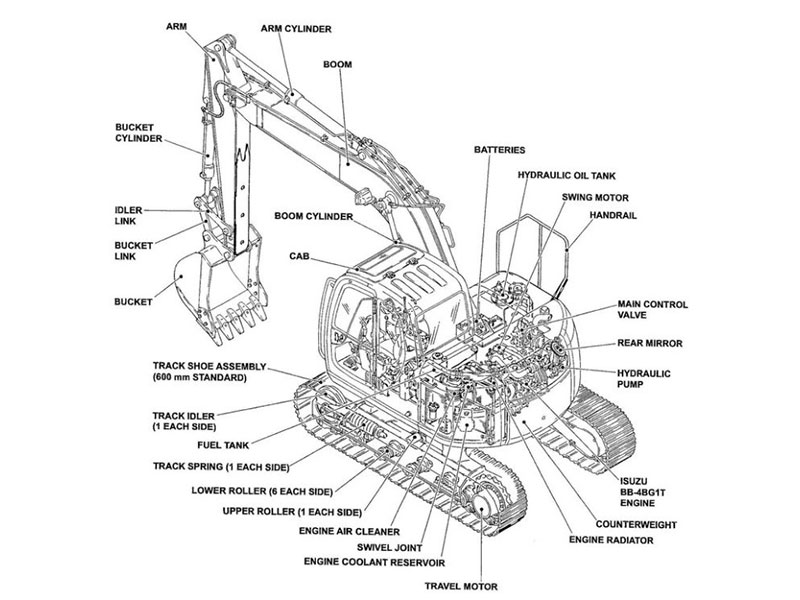
The main parts of an excavator include final drives, swing gear, track chains, idlers, track frame, hydraulic system, boom, arm, bucket, engine, counterweight, linkage gears, and crucial excavator gear parts. Each component plays a specific role. Final drives make the tracks move, while swing gear turns the upper structure. Track chains enable the excavator to move forward and backward, and idlers guide the tracks smoothly. The track frame supports the entire machine. The hydraulic system powers the movement of the boom, arm, and bucket. The engine supplies power to the excavator, and the counterweight keeps it balanced during operation. Linkage gears connect and articulate the working parts, and various excavator gear parts ensure smooth and efficient mechanical function. The table below outlines the main parts of an excavator and their functions:
Part | Function |
|---|---|
Final Drives | Propel tracks for movement |
Swing Gear | Rotates upper structure |
Track Chains | Enable forward and backward motion |
Idlers | Guide and support track chains |
Track Frame | Holds undercarriage components |
Hydraulic System | Powers movement of working components |
Boom | Lifts and moves arm and bucket |
Arm (Stick) | Extends bucket reach |
Bucket | Digs and scoops material |
Engine | Supplies power to all systems |
Counterweight | Balances the machine during operation |
Linkage Gears | Connect and articulate working parts |
Excavator Gear Parts | Ensure smooth mechanical operation |
Understanding these excavator parts, including essential excavator gear parts, helps workers maintain safety. It allows them to identify potential issues and keep the machine running efficiently. Learning about these components reduces risks and promotes proper care of the excavator.
Key Takeaways
Excavator parts like final drives, swing gear, track chains, and hydraulic systems all work together. They help the machine move and work well.
Doing regular maintenance is important. You should check oil, grease moving parts, and look for wear. This helps stop breakdowns and keeps the excavator safe.
Keeping the track tight and cleaning undercarriage parts is important. This stops damage and keeps the excavator steady while working.
Picking the right bucket is important. Taking care of the boom, arm, and linkage gears helps the excavator dig and lift better.
The counterweight helps balance the machine. Watching the hydraulic systems makes lifting safe and keeps the excavator steady.
Excavator Gear Parts

The undercarriage has many important gear parts. These parts help the excavator move and stay steady. They also help the machine work well. Knowing about each part helps operators take care of the machine. This can stop breakdowns.
Final Drives
Final drives help the tracks move. They change power from the engine or hydraulics into torque. This torque turns the tracks. It lets the excavator go forward or backward. The gears inside the final drive make more torque. This helps the machine carry heavy loads. It also helps control speed. Final drives send power to both tracks. This keeps the excavator balanced and steady.
Main functions of final drives:
Send power from the hydraulic motor to the tracks.
Make more torque for better grip and force.
Spread the load for better balance.
Change track speed for different jobs.
Tip: Operators should listen for strange sounds from the final drives. Grinding or whining noises can mean worn gears or bearings. Check for leaks, shaking, or too much heat. Keep the undercarriage clean. Check gear oil every 100 hours. Change filters as needed to stop big repairs.
Swing Gear
The swing gear lets the top of the excavator turn. It gets power from the hydraulic motor. It changes this power into smooth turning. This is important for digging and moving things. The swing gear is made to turn exactly, even in small spaces.
The swing gearbox and reduction gear control speed and direction.
Good alignment and oil help the swing gear work well.
The swing gear’s strength helps the operator move the excavator safely.
Signs of swing gear wear:
Strange noises like grinding or clunking.
Too much shaking or sticking when turning.
Leaking oil or getting too hot.
Note: Check the swing gear, bearings, and oil system often. Use good oil and follow the maker’s plan. Clean the area to keep out dirt and damage.
Track Chains
Track chains are strong steel links in a loop. They hold up the excavator and help it grip the ground. The track chains can bend and move with heavy loads.
Track chains work with sprockets and rollers to move the excavator. They always touch the ground. This helps the excavator stay steady and move smoothly. Keeping the right tension stops the tracks from coming off and wearing out.
Best practices for track chain maintenance:
Do regular maintenance checks.
Use a system to track checks and repairs.
Give each set of track chains a special number.
Teach workers to spot early signs of damage.
Use sensors to watch performance and update records.
Tip: Operators should check track tension at the start of each shift. Too much tension wears out the tracks. Loose tracks can sag or come off.
Idlers
Idlers are big wheels at the front of the undercarriage. They guide the track chains and keep the right tension. The shape of the idler keeps the track straight. This helps other parts last longer. Idlers work with track springs to set the right tension.
Good bearings and seals keep out dirt and water.
The idler’s spot and shape help the whole undercarriage work better.
Common causes of idler failure:
Not enough care or oil.
Uneven loads or wrong setup.
Old seals that let in water or dirt.
Wrong track tension.
Prevention tips:
Check idlers and other parts often.
Use the right grease for oiling.
Clean off mud and dirt after using.
Fix track tension when needed.
Replace broken or worn parts fast.
Track Frame
The track frame is the base of the undercarriage. It holds the tracks, idlers, rollers, and other parts. The track frame spreads the weight over a big area. This stops the excavator from sinking and helps it stay steady on soft ground.
The track frame takes in shocks and shaking. This protects other parts.
It works with track pads, chains, bolts, and guards to keep things lined up.
Inspection and maintenance tips:
Check the undercarriage every week or 40 hours.
Look at track wear and adjust every day.
Clean the undercarriage a lot, especially in winter.
Fix track tension to stop extra wear.
Tighten bolts and oil moving parts often.
Note: Operators should keep good records of checks and repairs. Finding problems early helps the track frame and other excavator gear parts last longer.
Table: Key Undercarriage Parts and Their Functions
Part | Function | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|---|
Final Drives | Move tracks, make more torque, control speed | Check oil, listen for noise, inspect |
Swing Gear | Turn the top part | Oil it, check for wear |
Track Chains | Hold weight, help grip | Check tension, look for wear |
Idlers | Guide tracks, keep tension | Oil, clean, fix tension |
Track Frame | Hold and line up undercarriage parts | Check, clean, tighten bolts |
All these excavator gear parts work together to help the machine move well and last long. Checking and caring for these parts stops breakdowns. It keeps the excavator safe and working right.
Hydraulic and Power Parts
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system gives the excavator its power. It helps the machine move with control. The main hydraulic pump changes engine power into hydraulic pressure. Oil under pressure moves through hoses and valves. This oil goes to different parts of the excavator. Hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors use this pressure. They move the boom, arm, bucket, and tracks. The main hydraulic pump must work well. This keeps the excavator working smoothly.
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Hydraulic Pump | Changes engine power into hydraulic energy by making oil pressurized. |
Hydraulic Valves | Guide and control where hydraulic oil goes. |
Hydraulic Cylinders | Turn hydraulic pressure into straight movement for boom, arm, and bucket. |
Hydraulic Motors | Turn hydraulic pressure into spinning movement for tracks and upper part. |
Reservoir | Holds clean hydraulic oil and keeps it ready. |
Pressure Regulator | Keeps hydraulic pressure steady and safe. |
The hydraulic system needs regular care. Operators should check fluid levels often. They should look for leaks and keep the oil clean. Problems can be low fluid, leaks, or overheating. Changing filters and checking parts often helps stop breakdowns.
Main Control Valves
Main control valves are like the brain of the hydraulic system. These valves send oil and pressure to each part of the excavator. When the operator moves the controls, the valves open or close. This sends oil to the right cylinder or motor. This lets the excavator dig, lift, or swing with control.
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Main Control Valve | Sends hydraulic fluid to tools and engine for movement. |
Actuators | Change hydraulic pressure into movement for gears and cylinders. |
Piston | Controls oil pressure and flow for smooth work. |
Spring | Holds the valve in place and softens shocks. |
Adjusting Screw | Fine-tunes flow and pressure for best work. |
If main control valves have problems, the excavator may move slowly or jerk. Operators might see leaks, sticking, or pressure changes. Cleaning and changing filters often keeps the valves working well.
Tip: If the excavator is slow or leaks oil, check the main control valves for blockages or worn parts.
Engine
The engine is the heart of the excavator. It gives power to the main hydraulic pump and final drive. Most excavators use diesel engines. Diesel engines give strong, steady power for hard jobs. The engine turns the main hydraulic pump. This pump powers the hydraulic system. The engine also moves the final drive gears. This makes the tracks and gear parts move.
Good engine performance means using less fuel and being reliable. It should work well under high pressure and heat. Operators should check coolant, oil, and air filters often. Common problems are overheating, trouble starting, or losing power. Doing regular maintenance, like changing filters and using clean fuel, helps stop these problems.
Operators should listen for odd noises and watch for smoke or leaks. Acting fast can stop bigger engine problems.
Working Parts of an Excavator

Boom
The boom is the main arm on the excavator. It sticks out from the machine’s body. The boom helps the excavator reach up high or far away. It holds the arm and bucket in place. Operators use the boom to dig or lift things that are not close. Hydraulic cylinders move the boom up and down. These cylinders give strong power for careful control. The boom’s shape and hydraulics decide how deep it can dig or how much it can lift. The boom, arm, and bucket work together for many jobs on different ground.
The boom gets its strength from hydraulic pressure. This pressure lets the boom lift heavy things and dig hard ground. The speed of the boom depends on the flow of hydraulic oil. Some systems make the boom move faster for big jobs. Safety parts like anti-rupture valves keep the boom steady if a hose breaks.
Checking the boom often helps stop damage. Operators should look for cracks or weak metal. Keeping the hydraulics in good shape stops leaks and pressure drops. Greasing joints and bearings every 50 to 100 hours cuts down on wear. Changing filters and checking hoses every 250 to 500 hours keeps the boom safe.
Arm (Stick)
The arm, or stick, links the boom to the bucket. The stick turns at its joint with the boom. This lets the operator move the bucket closer or farther away. The stick controls how high or far the bucket can go. Stick cylinders use hydraulics to move the arm in and out. This gives the operator careful control for digging and lifting.
Operators use the stick cylinder with the boom and bucket for smooth moves. Joystick controls help make small changes to speed and position. Different stick shapes help the excavator do more jobs. The stick’s joint and hydraulics help with digging, loading, and spreading.
Operators should check if the arm is straight and lined up. Cleaning the arm and joints gets rid of dirt that causes wear. Greasing moving parts with the right grease stops rust and cuts friction. Operators should not overload the arm to avoid bending or breaking. Changing worn or broken parts keeps the arm strong and safe.
Bucket
The bucket is at the end of the arm. It does most of the digging and loading. The bucket scoops, lifts, and moves dirt, rocks, and other stuff. Operators use the bucket for grading, finishing, and moving things. The bucket cylinder opens and closes the bucket. This gives the operator power and control for each scoop.
Different buckets work better for certain jobs. Big buckets move more dirt, which is good for loose soil. Small buckets are better for tight spaces. The bucket’s shape and teeth help it dig well. Standard teeth are for normal digging. Rock teeth are for hard or rough ground. Chisel teeth help with careful work.
Special buckets like micro trenching, skeleton, rake riddle, cleanup, and tilt buckets help with special jobs. Picking the right bucket for the job and machine makes work safer and faster.
Cause of Bucket Wear/Damage | Description | Effective Maintenance Strategies |
|---|---|---|
Abrasion | Rubbing on rocks and sand makes bucket walls thin. | Use wear strips and shrouds; check often. |
Impact | Hitting hard things makes dents or cracks. | Add shrouds; avoid hard hits. |
Corrosion | Water and chemicals cause rust. | Use coatings; store in dry places. |
Scratching | Sharp things make grooves. | Use wear plates; check for damage early. |
Fatigue | Doing the same work over and over makes cracks. | Check and fix fast. |
Cracking | Cracks from hard hits or stress. | Find and fix cracks early. |
Temperature Fluctuations | Hot and cold make metal weak. | Store buckets right; use strong materials. |
Operators should check the bucket often. They should look for thin spots, cracks, or broken teeth. Greasing the bucket’s joints and changing worn parts helps it last longer.
Linkage Gears
Linkage gears join the boom, arm, and bucket. These gears move force from the hydraulic cylinders to the working parts. Pins and bushings in the linkage help things move smoothly. Linkage gears help the excavator dig, lift, and move things with care.
Problems with linkage gears can be worn pins, bushings, or gears. Not enough grease and dirt can make them wear out faster. Broken pins or bushings make the movement loose and hard to control. Too much weight on the excavator puts extra stress on the linkage.
Operators should grease the linkage gears often. They should check pins and bushings every day. Changing worn parts and using good gear oil keeps the linkage working well. Not overloading the machine helps stop early breakdowns. Good care of linkage gears makes the excavator work better and safer.
Counterweight
The counterweight is at the back of the excavator. It balances the boom, arm, and bucket when digging or lifting. The counterweight keeps the excavator steady, even when the boom is stretched out. Makers design the counterweight’s size and spot to fit the machine’s weight and lifting needs.
Counterweights use heavy stuff like cast iron. This gives the right weight without making the machine too big. The right counterweight helps the excavator lift better and not tip over. Some counterweights can be taken off for easy moving and setup.
Operators should check if the counterweight fits right. A loose or wrong counterweight can shake and make the machine unsteady. Keeping the center of gravity low and steady helps stop accidents.
The counterweight and linkage gears work together to keep the excavator safe and working well. The counterweight gives balance, and the linkage gears help with smooth, careful moves. Both are important for safe digging, lifting, and moving heavy things.
Excavator Parts Functions
Movement Functions
An excavator moves because of several important parts. The final drives give power to the tracks. Track chains and idlers help it go forward and backward. The track frame holds the weight and keeps it steady on bumpy ground. The hydraulic system makes the tracks and top part move. The swing gear lets the top turn left or right. All these parts work together for smooth movement.
Operators check these parts often for problems. They look for things that are broken or worn out. Taking care of these parts keeps the excavator safe and ready. Good movement is important for safety and getting work done fast.
Digging Functions
The boom, arm, and bucket help the excavator dig and move things. The hydraulic system moves these parts with strong force. The boom goes up and down. The arm reaches out and pulls back. The bucket scoops, lifts, and dumps dirt or rocks. Linkage gears join these parts and help them move easily.
Digging lets the excavator break hard ground and lift heavy stuff. Operators pick the right bucket for each job. They look for cracks or worn teeth on the bucket. Checking these parts often keeps the excavator strong and working well.
Lifting and Stability
Lifting heavy things is an important job for an excavator. The boom, arm, and bucket work together to lift and move stuff. The counterweight at the back helps keep the machine balanced. The track frame spreads out the weight and helps it stay steady. Hydraulic cylinders give the power needed to lift safely.
Operators need to know how much the excavator can lift. They do not try to lift things that are too heavy. Good balance keeps the machine from tipping over. Safety checks and using each part the right way protect the operator and the machine.
Tip: Always check the counterweight and track frame before lifting. A steady excavator works better and keeps everyone safe.
Function | Key Parts Involved | Impact on Performance and Safety |
|---|---|---|
Movement | Final drives, track chains, idlers, swing gear, hydraulic system | Smooth travel, safe operation |
Digging | Boom, arm, bucket, linkage gears, hydraulic system | Strong digging, reliable material handling |
Lifting/Stability | Boom, arm, bucket, counterweight, track frame | Safe lifting, prevents tipping |
Knowing what each excavator gear part does helps operators keep the machine safe and working well. Checking and caring for the parts often makes them last longer and keeps everyone safer:
Make and use a checklist before, during, and after using the machine. This helps find damage early.
Watch track tension and clean the tracks every day. This stops the tracks from wearing out fast.
Look at fluids and filters daily to make sure everything is oiled right.
Write down all service and repairs to help keep the equipment worth more.
If the repair is hard, trained technicians and OEM parts help the excavator meet all rules. Doing these things helps every excavator work safely and without problems.
FAQ
What is the most important part to check on an excavator?
Operators need to look at the hydraulic system first. This system makes most parts move. If there are leaks or not enough fluid, big problems can happen. Checking it often helps stop breakdowns.
How often should operators grease excavator gear parts?
Operators should put grease on moving parts every 50 to 100 hours. Greasing stops parts from wearing out fast. It also helps the machine work well. Always use the schedule from the maker.
Why do excavator tracks come off during work?
Tracks can slip off if the tension is too loose or if track chains are worn out. Operators should check the tension every day. The right tension keeps tracks on and stops damage.
Can operators replace excavator buckets themselves?
Operators can change buckets if they follow all safety rules. They need to use the right tools and make sure pins are tight. If the bucket is broken or very heavy, a technician should help.