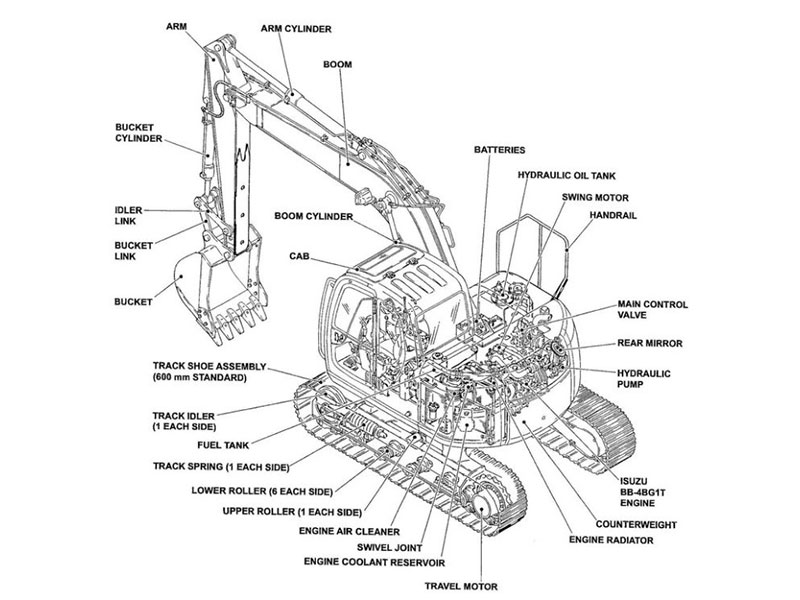
Excavator electrical parts are very important for how the machine works every day. The main parts are the ECU, sensors, wiring harnesses, batteries, alternator, relays, fuses, display panels, electric motors, and the main control valve. These parts work together to control power, check systems, and keep the machine safe. New electric excavator technology helps the machine run smoother, use less energy, and be safer by lowering noise, shaking, and exhaust fumes.
Key Takeaways
Excavator electrical parts like the ECU, sensors, wiring harnesses, batteries, and electric motors all work together. They help control power, watch over systems, and keep the machine safe.
Checking and taking care of wiring, batteries, relays, and fuses often helps stop electrical problems. This keeps the excavator working well.
New excavators use smart sensors and control units. These make the machine work better, use less fuel, and stay safer with things like collision avoidance and emergency stops.
Electric and hydraulic systems work together to save energy. They also make less noise and lower pollution. This makes excavators work better and helps the environment.
Finding and fixing electrical problems early helps stop long breaks. It also helps the machine last longer and lets workers finish jobs safely and on time.
Essential Excavator Electrical Parts

Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The electronic control unit is like the brain of the excavator. It gets information from sensors and tells other parts what to do. There are different types of electronic control units for different jobs.
Engine management ECUs help control fuel and timing. This makes the engine stronger and cleaner.
Hydraulic control ECUs help move hydraulic fluid. This makes the machine move smoothly.
Transmission control ECUs help change gears. This gives the machine more power and saves energy.
Diagnostic ECUs check if the excavator is healthy. They can warn about problems and help with repairs.
Safety ECUs help stop the machine in emergencies. They also help avoid crashes and keep the machine steady.
For example, the SPARKLING CX130DLC ECU in CASE CX-series excavators controls many things. It helps with engine power, fuel, hydraulics, and checks for problems. This ECU helps the excavator use less fuel and work well even when it is hard.
Sensors
Sensors are important for checking how the excavator is working. They collect data and send it to the electronic control unit. The electronic control unit uses this data to make choices. Some common sensors are:
Sensor Type | Parameters Monitored / Application |
|---|---|
Temperature Sensors (RTD) | Engine and hydraulic fluid temperature |
Pressure Sensors | Hydraulic and pneumatic system pressures |
Proximity Sensors | Detect nearby objects for collision avoidance |
Level Sensors | Fuel and hydraulic fluid levels |
Flow Sensors | Fluid flow rates in fuel and hydraulic systems |
Absolute Encoders | Boom, bucket, and upper structure positioning |
Dynamic Inclination Sensor | Boom positioning |
Strain Sensors | Load measurement, bucket fill factor |
Absolute Magnetic Encoder | Steering angle determination |
Coolant Sensors | Coolant temperature and flow |
Other sensors, like accelerometers and geophones, check for shaking. This helps protect buildings and keeps people safe. These sensors help the electronic control unit keep the excavator working safely.
Wiring Harnesses
Wiring harnesses link all the electrical parts together. They send power and signals between the electronic control unit, sensors, batteries, electric motors, relays, and the fuse box. The wires are made to be strong and bend easily. They have thick covers to protect them from heat.
Wiring harnesses often have extra covers to stop shock, shaking, and dirt. Special shields block unwanted electrical noise. Wires are colored and easy to fix. Strong connectors and clamps help wiring harnesses last longer.
Designers follow rules like ISO 16750 and SAE J1939 for safety. Wiring harnesses are tested for shaking, pulling, and water. Most can handle very hot or cold weather and high voltages. If there is power loss, shorts, or rust, the wiring harness can fail. It is important to check them often.
Electric Motors
Electric motors help move many parts of the excavator. They power the tracks, pumps, and other moving parts. There are different kinds of electric motors used in excavators.
Motor Type | Main Applications | Key Benefits and Features |
|---|---|---|
Battery-powered Electric Drive | Driving tracks, hydraulic systems | Zero emissions, low noise, instant torque, powered by lithium-ion batteries |
Regenerative Braking Systems | Energy recovery during braking | Recovers energy, improves efficiency |
Hybrid Systems (Diesel + Electric) | Combines diesel and electric power | Energy efficiency, reduced emissions, better performance |
Stepper and Servo Motors | Precision control of valves and components | High precision, quick response, accurate control |
Synchronous Permanent Magnet | High power output for large equipment | Powerful but can overheat |
Induction (Asynchronous) | Reliable, affordable, used in some vehicles | Robust but less efficient in power surges |
Synchronous Reluctance | Used in large excavators | Lower cost, handles power surges, less noise |
Brushless Motors | Heavy-duty applications | Rugged, reliable, space-saving |
Electric motors are more efficient than hydraulic systems. They save energy, make less noise, and lower pollution.
Alternator and Battery
Batteries store power and help start the engine. They also run lights and control systems. The alternator makes electricity when the engine is on. It charges the batteries and powers other parts. In electric and hybrid excavators, batteries also run electric motors and big systems.
Checking batteries and alternators often helps stop power problems. Weak batteries or a bad alternator can make the machine hard to start or cause it to shut down.
Relays and Fuses
Relays and fuses keep electrical parts safe from harm. Relays are switches that use a small signal to control bigger currents. This lets the electronic control unit turn on or off big devices from far away. Relays also keep control circuits and power circuits apart for safety.
Fuses are safety parts that stop too much current. If too much power goes through, the fuse melts and stops the electricity. This keeps wires, batteries, and other parts safe from fire or damage. Excavators have a fuse box to keep circuits safe. The ac box with fuses protects air conditioning and related systems.
Checking relays and the fuse box often helps stop electrical problems. Blown fuses, loose wires, or rusted ends are common issues. If a relay or fuse breaks, lights, panels, or motors may stop working.
Main Control Valve
The main control valve works with electrical parts to move the excavator. When the operator moves the joystick or pedals, signals go through wiring harnesses to electric valve blocks. These blocks control hydraulic pistons by changing fluid flow and pressure. Some excavators use special poppet valves for better control.
The electronic control unit and main control valve work together. They match engine speed and hydraulic power to the job. This teamwork helps the excavator move smoothly and quickly.
How Excavator Electrical Parts Work Together

Power Generation and Distribution
Excavators need a strong electric system for steady power. The electric excavator uses batteries to store energy. These batteries give out energy when the machine works. Charging starts when the operator plugs in the charger. The batteries fill up with energy for the next job. Some machines have a 2N system with two power sources. If one power source fails, the other keeps things running. Circuit breakers and relays protect the system from problems. The charging process must work well to stop downtime. Checking batteries, alternators, and wiring often helps avoid slow starts or power loss. The charging process also means looking for broken wires or connectors. Damaged wires can cause shorts or make the system fail.
Control and Monitoring
Power and control systems work together to move the excavator. The electronic control unit gets data from sensors. It sends commands to motors and valves. Real-time monitoring checks speed, load, and machine health. GPS tracking shows where each excavator is used. Alerts warn operators if something is wrong during charging. Alerts also warn if batteries need care. Modern systems use IoT sensors and telematics for updates. These updates go to remote teams. This technology helps stop downtime and keeps the system working. Data from these systems helps improve charging. It also helps make better choices for future jobs.
Safety and Protection
Safety is very important in every electric system. Excavators have many safety features for the machine and operator. Hydraulic safety interlocks stop the machine if controls are not right. Seatbelt monitors remind operators to buckle up. Swing control protection, like E-fence, keeps movement in safe zones. Rearview cameras and alarms help stop accidents. The charging process has safety checks to stop electrical dangers. Good grounding and ground-fault circuit interrupters stop shocks. Regular maintenance and training keep the system safe. The table below lists some key safety features:
Safety Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
Hydraulic Safety Interlock | Stops machine operation unless controls are set correctly. |
Seatbelt Monitor Switch | Reminds operator to use seatbelt for safety. |
Swing Control Protection (E-fence) | Limits boom movement to safe zones. |
Rearview Cameras | Improves visibility and reduces blind spots. |
Alarm Systems | Alerts people nearby when the machine moves. |
Safety Courtesy Lights | Lights up the area for better visibility during low light. |
System Integration and Efficiency
Electrical and Hydraulic Coordination
Modern excavators need electrical and hydraulic parts to work together. This teamwork helps the machine use less energy. It also makes the machine run smoother. Experts say mixing electric and hydraulic systems is better for the environment. These systems make excavators use less fuel and create less pollution. Digital hydraulic actuators have sensors and electronics. They help make machines more automatic. These parts are smaller and waste less energy. Smaller parts give more room for batteries. This means the machine does not need a huge battery.
Volvo’s electric-over-hydraulic system is a good example. It uses smart cooling and engine speed control. This can save up to 15% more fuel. Operators can pick work modes for each job. This gives them better control and smoother moves. The system only uses hydraulic power when needed. This saves energy and cuts down on waste. Dr. Steffen Mutschler found that saving and reusing energy from movements can cut energy use by 40%. Using an electric drive instead of a diesel engine saves even more energy. Adding a special electric motor for turning can save another 46%. This almost doubles how long the battery lasts. Using both hydraulic power and electric drive makes the excavator better. It becomes more accurate, uses less energy, and is better for the planet. The hvdu helps both systems work together well.
Advanced Features and Diagnostics
New excavators have smart features to help operators and technicians. These features use sensors and hvdu systems to check the machine’s health all the time. Heavy Vehicle Inspection technology finds problems before the machine breaks. Predictive maintenance apps use data to find issues early. This means repairs can happen before something goes wrong.
Smart sensors and hvdu systems check the machine’s health in real time.
Predictive tools help plan repairs before things break.
AI and machine learning make these tools smarter.
Big data helps people make better repair choices and keep machines working longer.
Training helps operators use these new tools the right way.
These features also help the environment by making machines cleaner and more efficient.
Modern excavators use scanning and mapping tools to find things underground. Better communication between machines helps work go faster. Strong and explosion-proof parts make excavators safer, especially in mines. These new features help owners get more from their machines. They lower downtime and make machines more reliable.
Essential Electric Parts Maintenance
Inspection and Care
Checking the excavator often helps it work well and safely. Operators should look at the electric control box and wiring system a lot. This helps stop short circuits from old wires or wetness. Manufacturers say to check the electrical system every 1,000 hours. Sensors and instruments need to be set right at the same time. This keeps their readings correct. Operators should keep extra electric parts ready for emergencies.
Look at wiring harnesses for damage, loose ends, or rust.
Clean wires and connectors to get rid of dirt and water.
Make sure all wires are tight so they do not break.
Cover wires with things like conduit or heat shrink tubing.
Follow the care schedule for each part.
Tip: After working in tough places, always check and clean the wiring harness. This helps stop problems later.
Common Issues
Excavators can have many electrical problems. Batteries might make starting hard or need charging a lot. Sensors can give strange readings or turn on warning lights. Wiring harnesses can break if you see damage or smell burning. Control panels may not work or show error messages. Circuit failures, motor failures, and electronic control unit faults happen too. Most problems come from bad connections, short circuits, or old wires.
Problem Area | Signs of Failure |
|---|---|
Battery | Hard to start, needs charging often |
Sensors | Warning lights, strange readings |
Wiring Harness | Power loss, damage, burning smell |
Control Panel | No response, error messages |
Troubleshooting Tips
Operators can fix many electrical problems with easy steps. First, check all wires and connectors for damage or loose parts. Clean battery ends and make sure they are tight. Change old batteries that do not keep a charge. Use a multimeter to check circuits and parts. If something is broken, use the guide to fix or change it. Always keep parts safe from dust, water, and very hot or cold weather.
Note: Finding problems early and fixing them fast helps stop bigger issues. This keeps the excavator safe when charging and working.
Taking good care of electric parts helps the excavator work better and safer. Regular care means less downtime and a longer life for the machine.
Understanding how each excavator electrical part works helps operators keep the machine safe. Checking batteries, wiring, and relays often helps teams find small problems early. Small issues can be fixed before they turn into big breakdowns. If lights look dim or warning signals turn on, the excavator needs attention. New tools like IoT sensors and digital records help crews find problems quickly. These steps help the excavator last longer and cost less to fix. They also help jobs finish on time. Operators who know their excavator’s systems can fix problems fast and keep the machine working well.
FAQ
What does the electronic control unit (ECU) do?
The ECU is like the machine’s brain. It gets information from sensors. It tells other parts what to do. This helps the machine work well and stay safe.
How often should operators check wiring harnesses?
Operators need to check wiring harnesses every 1,000 hours. They should look for broken wires or loose ends. Checking often helps stop electrical problems.
Why do sensors matter in heavy equipment?
Sensors watch things like heat, pressure, and movement. They send this information to the ECU. The ECU uses it to help the machine work better and safer.
What are signs of a failing battery or alternator?
A weak battery or bad alternator can make starting slow. Lights might get dim. Warning lights may show up on the screen. Operators should change bad parts fast.
How do relays and fuses protect the system?
Relays use small signals to control big power. Fuses stop too much power from hurting parts. Both help stop fires and keep the excavator safe.