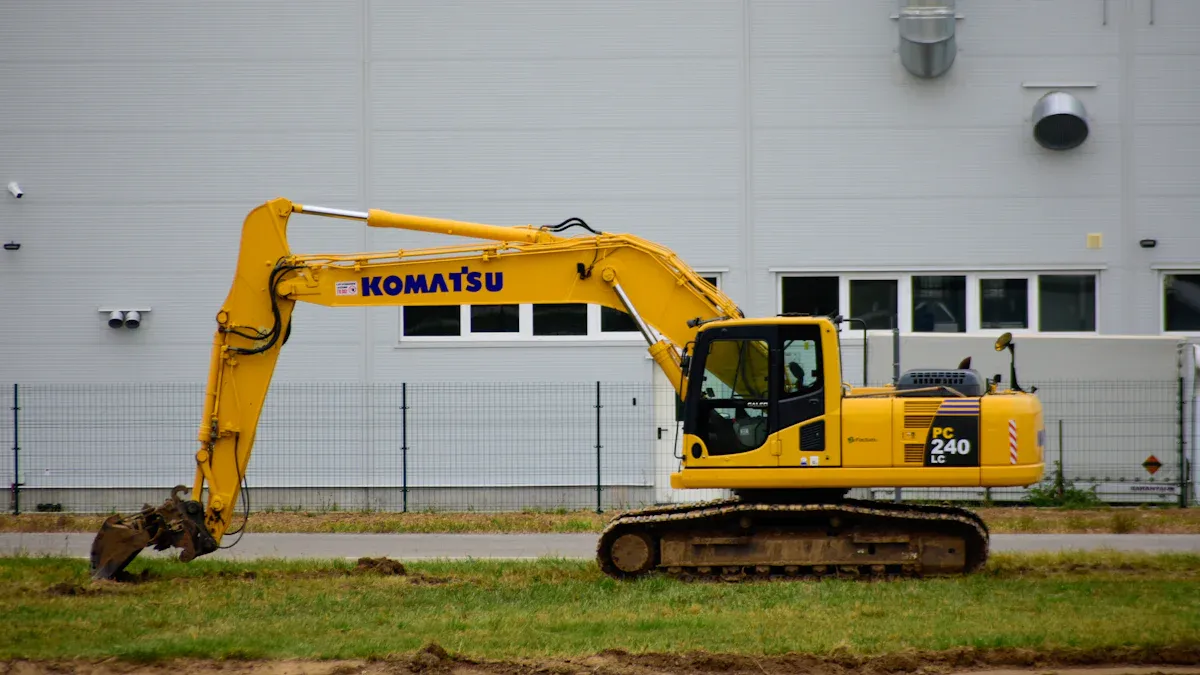
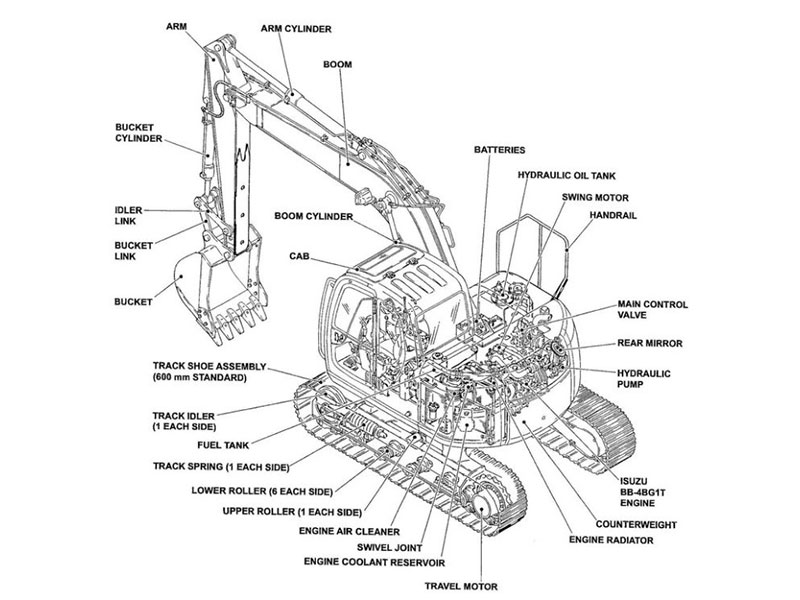
Excavators feature three main components: the undercarriage, the house, and the arm assembly.
The undercarriage provides stability and mobility, allowing excavators to move across challenging terrain.
The house contains controls and the engine, supporting safe operation.
The arm assembly performs digging and lifting, making excavators essential for many tasks.
Understanding the parts of an excavator helps operators maximize the benefits of using excavators and informs decisions when choosing china excavator structural component part suppliers. Knowledge of the main components of an excavator also supports safe and effective work and highlights the diverse uses of excavators.
Key Takeaways
Excavators have three main parts: the undercarriage for stability and movement, the house for controls and power, and the arm assembly for digging and lifting.
A strong undercarriage keeps the machine steady on rough ground, while the house offers operator comfort and machine balance through its rotating design.
The arm assembly uses hydraulic power to control the boom, stick, and bucket, allowing precise and powerful digging and lifting.
Regular inspection and maintenance of parts like tracks, hydraulic hoses, and the engine prevent breakdowns and improve safety.
Choosing reliable suppliers, especially from trusted sources in China, ensures high-quality parts, reduces costs, and extends excavator life.
Main Components of an Excavator
Excavators stand out as powerful machines because of their well-designed structure. The main components of an excavator include the undercarriage, the house (upper structure), and the arm assembly. Each group plays a unique role in the anatomy of excavators, working together to deliver strength, precision, and reliability on job sites.
Undercarriage
The undercarriage forms the foundation of the machine. It supports the entire weight of the excavator and allows it to move across rough ground. Tracks and rollers help distribute weight evenly, giving the machine stability and traction. The undercarriage also absorbs shocks and vibrations, protecting other parts of an excavator from damage. Operators rely on a strong undercarriage to keep the machine steady during digging and lifting.
House (Upper Structure)
The house sits above the undercarriage and rotates 360 degrees. It contains the cab, engine, hydraulic system, and control panels. The operator controls the excavator from the cab, which offers comfort and safety features. The engine compartment powers all movements, while the hydraulic system delivers force to the arm assembly. The house also holds the counterweight, which balances the machine during heavy lifting. This section connects all major parts and allows for smooth, efficient operation.
Arm Assembly
The arm assembly performs the main digging and lifting tasks. It includes the boom, stick, and bucket, which work together to move soil, rocks, and debris. The hydraulic system powers the arm assembly, providing precise control and strong force. Operators can attach different tools to the arm, making excavators versatile for many jobs. The arm assembly’s design allows for deep digging, high reach, and accurate placement of materials.
Operators and fleet managers benefit from advanced features in each component group. For example, variable displacement pumps and load-sensing systems in the hydraulic system reduce fuel use and increase productivity. Ergonomic controls and enhanced visibility in the cab improve safety and reduce fatigue. Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics help extend equipment life and lower costs.
Component Group | Efficiency and Operational Benefits |
|---|---|
Hydraulic Systems | Variable displacement pumps and load-sensing systems reduce fuel consumption and improve precision, increasing productivity. |
Telematics & Remote Monitoring | Real-time diagnostics and fleet management improve maintenance response and operational efficiency. |
Automation & Smart Controls | Automated grade control and bucket placement systems increase accuracy, reduce errors, and speed up operations. |
Hybrid & Electric Power Systems | Hybrid systems improve fuel efficiency by up to 30%, reduce emissions, and lower operating costs. |
Operator Comfort & Safety | Ergonomic controls, enhanced visibility, collision avoidance, and automatic shutdown systems reduce fatigue and improve safety. |
Fuel Management Technologies | Fuel flow meters and advanced filtration reduce fuel consumption and emissions, extending engine life. |
Cycle time and idle time analyses help identify inefficiencies and optimize coordination between excavation and hauling.
Real-time alerts and predictive analytics support proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending the life of key parts.
Monitoring dashboards give managers a clear view of equipment health, leading to better decisions and safer operations.
The main components of an excavator work together to deliver high performance, safety, and efficiency. Understanding the parts of an excavator helps users select the right machine and maintain it for long-term success.
Undercarriage of Excavators

The undercarriage forms the base of all excavators. It supports the house and arm assembly, giving the machine stability and mobility on different terrains. Each part of the undercarriage plays a unique role in the performance and safety of the excavator.
Tracks and Track Chains
Tracks and track chains help excavators move across mud, gravel, and uneven ground. These parts of an excavator spread the machine’s weight, preventing it from sinking or tipping. Engineers use statistical durability metrics to measure how long these components last.
Wear depth (Δh) shows how much the track wears down over time.
Normal impact wear energy (En) and tangential impact wear energy (Et) measure the energy absorbed by the track during operation.
These metrics help predict when to replace excavator tracks and track frame components, keeping the machine safe and efficient.
Rollers and Idlers
Rollers and idlers guide and support the tracks as they move. They keep the tracks aligned and help distribute the excavator’s weight. There are two main types of rollers: single flange (SF) and double flange (DF). The table below compares their features:
Feature | SF Track Roller | DF Track Roller |
|---|---|---|
Carrying Capacity | Up to ~15 tons | Up to ~80 tons |
Side Impact Resistance | Medium | Excellent |
Maintenance Cycle | 200-400 hours | 500-800 hours |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
DF rollers handle heavy loads and rough terrain better, making them ideal for large excavators. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and inspection, extends the life of these excavator parts.
Sprockets
Sprockets drive the tracks by engaging with the track links. They transfer power from the engine to the tracks, moving the excavator forward or backward. Worn sprockets can cause track slippage or uneven movement, so timely replacement is important for smooth operation.
Track Frame
The track frame holds all undercarriage parts together. It provides a strong base for the house and arm assembly. A well-built track frame ensures the excavator stays stable during digging and lifting. The durability of the track frame affects the overall lifespan of the machine.
A strong undercarriage supports the weight and movement of excavators, allowing them to work safely and efficiently in tough environments.
House and Key Parts of an Excavator
The house sits on top of the undercarriage and acts as the control center for the excavator. This section rotates a full 360 degrees, giving the operator the ability to work in any direction without moving the entire machine. The house contains several key parts of an excavator that support both performance and safety.
Cab
The cab provides a safe and comfortable space for the operator. Large windows give clear visibility of the work area. Manufacturers design seats with ergonomic support to reduce fatigue during long shifts. Modern cabs often include climate control, adjustable controls, and noise reduction features. These improvements help operators stay alert and productive.
Engine Compartment
The engine compartment houses the power source for the excavator. Diesel engines are common because they deliver strong torque and reliability. The engine powers the hydraulic system, which moves the arm assembly and other excavator parts. Easy access to the engine compartment allows for quick maintenance and inspection.
Counterweight
The counterweight sits at the rear of the house. It balances the weight of the arm assembly and bucket during digging or lifting. Proper balance prevents the excavator from tipping over. The size of the counterweight depends on the size and capacity of the machine.
Fluid Tanks
Fluid tanks store essential liquids such as fuel, hydraulic oil, and coolant. These fluids keep the engine running smoothly and the hydraulic system working efficiently. Regular checks of fluid levels help prevent breakdowns and extend the life of the excavator.
Swing Mechanism
The swing mechanism allows the house to rotate. This system uses a large bearing and hydraulic motor to turn the house smoothly. The swing mechanism gives the operator precise control over the position of the arm assembly. Quick and accurate rotation improves productivity on the job site.
A well-designed house improves operator comfort, machine balance, and overall efficiency. Understanding these key parts of an excavator helps users choose the right machine and maintain it for safe operation.
Arm Assembly and Hydraulic System
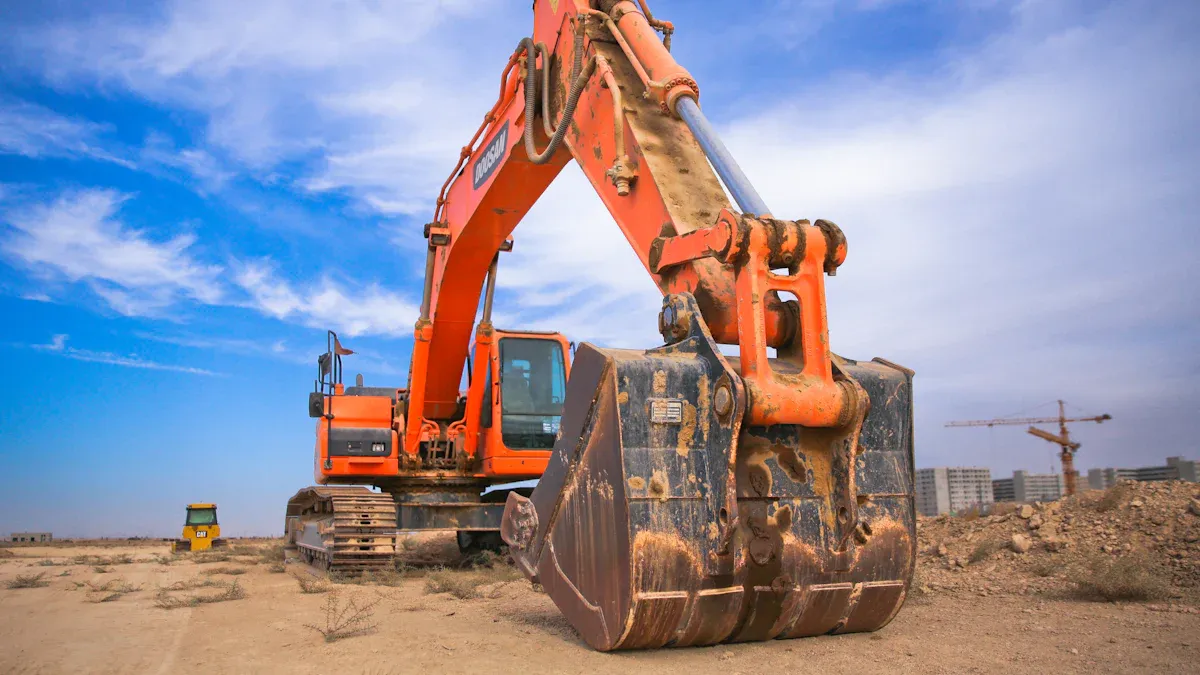

The arm assembly of an excavator handles the main digging and lifting tasks. This group includes the boom, stick, bucket, hydraulic cylinders, hoses, and various attachments. The hydraulic system powers each movement, giving operators control and strength for precise excavation tasks.
Boom
The boom acts as the primary structural arm of the excavator. It manages vertical lifting loads and determines the reach and lifting capacity. Manufacturers use high-tensile steel alloys to reinforce stress points, ensuring durability during heavy operations. Most booms range from 4.6 to 7 meters in length and feature a tapered box-section profile. This design helps the boom handle compressive and tensile forces during lifting and demolition work.
Stick (Arm)
The stick connects the boom to the bucket. It extends the excavator’s reach and controls the depth of excavation. Engineers design the stick to resist bending and shock loads, especially during tough digging or demolition jobs. The standard length ratio between boom and stick is about 1.5:1 to 1.8:1, which balances reach and stability. Sticks usually measure between 2.5 and 3.5 meters, with a uniform cross-section for strength.
Bucket
The bucket attaches to the end of the stick. It comes in many shapes and sizes, each suited for different materials and tasks. Some buckets are built for heavy-duty digging, while others handle fine grading or demolition debris. The bucket’s design directly affects digging efficiency and material handling.
Hydraulic Cylinders and Hoses
The hydraulic system uses cylinders and hoses to move the boom, stick, and bucket. Hydraulic cylinders provide up to 10,000 hours of reliable service, while hoses last between 1,000 and 2,000 hours. Operators must select hoses based on size, pressure rating, and temperature resistance. Proper reinforcement and minimum bend radius extend hose life, especially under constant flexing. Fittings must match hose type and size to prevent leaks. Material choice for fittings, such as carbon steel or stainless steel, depends on environmental conditions. Regular maintenance and high-quality parts keep the hydraulic system safe and efficient.
Hydraulic Component | Typical Lifespan (hours) |
|---|---|
Hydraulic Cylinders | Up to 10,000 |
Hydraulic Hoses | 1,000 to 2,000 |
Tip: Regular inspection and timely replacement of hydraulic hoses and cylinders prevent sudden failures and keep the excavator running smoothly.
Attachments
Attachments expand the capabilities of the arm assembly. Operators can switch between buckets, grapples, hydraulic breakers, and shears for different jobs. The hydraulic system powers these attachments, making the excavator versatile for demolition, trenching, and material handling. Quick couplers allow fast changes, saving time on the job site.
The synergy between the boom, stick, bucket, and hydraulic system ensures powerful, precise, and flexible performance for all excavation and demolition needs.
China Excavator Structural Component Part Suppliers
Sourcing Main Components
Selecting high-quality parts is essential for excavator performance and safety. Many companies turn to china excavator structural component part suppliers for cost savings and product variety. These suppliers offer a wide range of brands and models, including options from XCMG and SANY. Businesses can find components for mini, medium, and large excavators, as well as specialized attachments.
A strong supplier network in China provides several advantages:
Benefit Category | Evidence Summary |
|---|---|
Cost Savings | Up to 20% cost savings compared to local suppliers, providing competitive pricing without sacrificing performance. |
Product Variety | Wide selection of brands and models from top manufacturers like XCMG and SANY, covering mini to large excavators and related machinery. |
Quality Assurance | Partnerships with top factories, SGS inspections, extensive R&D teams (7,000+ staff at SANY), and warranties (e.g., 5-year warranties in some markets). |
Innovation & Sustainability | Advanced digitization, eco-friendly equipment (electric trucks, green mining support), and smart manufacturing processes. |
Global Support & Parts | Global dealer networks and thriving gray markets ensure availability of parts and services worldwide. |
Logistics & Import Support | End-to-end logistics handling, including shipping and customs clearance, reducing delays and import challenges. |
Tip: Many buyers use platforms like Alibaba to connect with verified sellers. Requesting video proof of equipment condition helps ensure transparency.
Choosing Reliable Suppliers
Working with trusted china excavator structural component part suppliers reduces risks and improves long-term value. Reputable suppliers follow strict testing protocols, such as ultrasonic scans, tensile strength tests, and visual inspections. They often hold certifications like ISO9001/2015 and ASTM, which signal a commitment to quality.
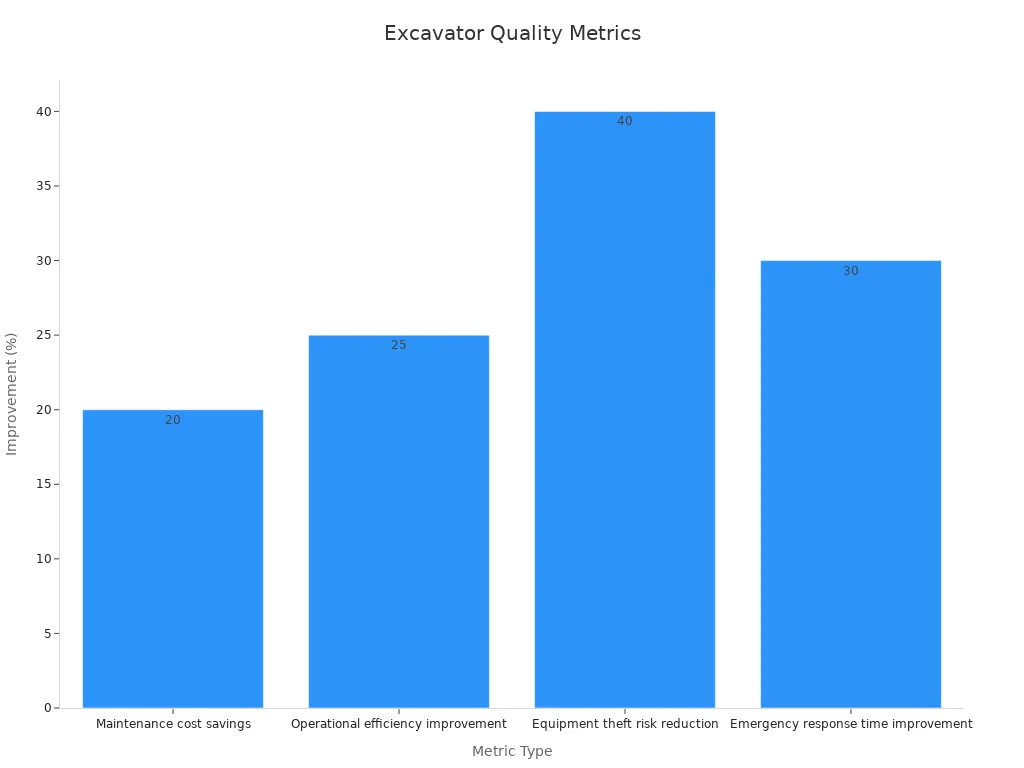
Reliable suppliers help reduce equipment downtime by up to 30% and lower maintenance costs by 20%. They use authentication methods like QR codes and tamper-evident packaging to prevent counterfeit parts. Long-term partnerships with china excavator structural component part suppliers can improve parts availability by 40% and reduce operational costs by 25%.
When choosing a supplier, consider these points:
Check for industry certifications and testing standards.
Ask for proof of product quality and warranty terms.
Evaluate logistics support, including shipping and customs handling.
Review customer feedback and after-sales service options.
Selecting the right china excavator structural component part suppliers ensures better equipment performance, longer lifespan, and fewer unexpected repairs.
Knowing the main structural components of excavators helps operators work safely and keep machines in top condition. Regular checks and maintenance prevent breakdowns and reduce accident risks.
In 2023, 310 machinery accidents caused 294 deaths, often from mechanical injuries.
Crawler and hydraulic parts can be dangerous if not handled properly.
Rollover risks increase on slopes or soft soil.
Inspections of the undercarriage, bucket, engine, and hydraulic system keep traction and stability strong.
This knowledge supports better troubleshooting, smarter sourcing of parts, and safer uses of excavators in demolition and other tasks. Operators gain the benefits of using excavators by staying informed and alert.
FAQ
What is the most important structural component of an excavator?
The undercarriage stands out as the most critical component. It supports the machine’s weight, provides stability, and enables movement across rough terrain. Without a strong undercarriage, the excavator cannot operate safely or efficiently.
How often should operators inspect excavator components?
Operators should inspect key parts daily before use.
Check tracks, rollers, and hydraulic hoses for wear.
Inspect the bucket and attachment pins.
Review fluid levels and engine condition.
Can operators replace excavator attachments easily?
Yes, most modern excavators use quick couplers. These allow operators to switch buckets or tools in minutes. This feature increases productivity and reduces downtime on job sites.
Why do excavators need counterweights?
Counterweights balance the machine during lifting and digging. They prevent tipping and improve safety. The size of the counterweight matches the excavator’s arm and bucket capacity.
Where can buyers find reliable excavator component suppliers?
Buyers can source parts from certified suppliers in China.
Look for ISO9001/2015 certification.
Request product testing reports.
Check customer reviews and after-sales support.